
More Details
01
MERI-TRP
Introduction
The Tympanoplasty Reporting Protocol (TRP) can be used to generate a numeric indicator of the severity of middle ear disease. An index of Middle Ear Risk (MER) can be used to stratify patient groups and allow more meaningful comparisons between different studies.
1. TRP: Tympanoplasty reporting protocol – minimum data set for publishing
2. MERI: Middle Ear Risk Index - a numeric indicator for severity of disease which is derived from a small subset of the TRP data
3. AK: Austin-Kartush Ossicular Classification
4. Stratifications to improve study comparisons
b. Hearing Outcome Categories
Good: 10 – 20db
Fair: 20 – 30db
Poor: > 30db
In 2001, there was a small update to add smoking as a risk factor and to increase the cholesteatoma risk from 1 to 2.
With this app we are now introducing the latest iteration, MERI Hybrid 2021.
The purpose of this change is twofold.
First, to improve MERI by adopting a number of key factors from the Black SPITE and Dornhoffer OOPS systems that were absent from the MERI.
-More precise delineation of diseased middle granulation tissue vs effusion / otorrhea
The second addition includes fields for more precise description of cholesteatoma. While there is no consensus, two systems have risen to international prominence. Rather than choose one arbitrarily, we include fields for both the EAONO/JOS as well as the ChOLE classification systems. See full references cited below.
MERI 2001 vs 2021 Hybrid Update
02
MERI-TRP
MERI Scores
MERI 2001 Risk Categories:
Mild pathology = 1-3
Moderate pathology = 4-6
Severe pathology => 7
MERI Hybrid 2021 Risk Categories:
Mild pathology = 1-3
Moderate pathology = 4-8
Severe pathology => 9
03
MERI-TRP
MERI Table
MERI 2001;
Dry = 0;
Occasionally wet = 1;
Persistently wet = 2;
Wet, cleft palate = 3
Perforation:
None = 0; Present = 1
Cholesteatoma:
None = 0; Present = 2
Ossicular Status:
0) M+I+S+ = 0;
A) M+S+ = 1;
B) M+S- = 2;
C) M-S+ = 3;
D) M-S- = 4;
E) Ossicular head fixation = 2;
F)Stapes fixation = 3
Middle ear granulation or effusion:
No = 0; Yes = 2
Previous surgery:
None = 0; Staged = 1; Revision = 2
Smoker:
No = 0; Yes = 2
MERI Hybrid 2021;
Otorrhea (Belluci):Dry = 0;
Occasionally wet = 1;
Persistently wet = 2;
Wet, cleft palate = 3
Perforation:
None = 0; Present = 1
Cholesteatoma:
None = 0; Present = 2
Ossicular Status:
0) M+I+S+ = 0;
A) M+S+ = 1;
B) M+S- = 2;
C) M-S+ = 3;
D) M-S- = 4;
E) Ossicular head fixation = 2;
F)Stapes fixation = 3
Middle ear granulation:
No = 0; Yes = 2
Middle ear fluid:
No = 0; Yes = 1
Previous surgery:
None = 0; Staged = 1; Revision = 2
Smoker:
No = 0; Yes = 2
Surgical interventions:
Tympanoplasty wo Mastoidectomy = 1; CWU = 2; CWD = 3
M malleus, I incus, S stapes, CWU Canal wall up, CWD Canal wall down.
04
MERI-TRP
Austin-Kartush Ossicular Classification
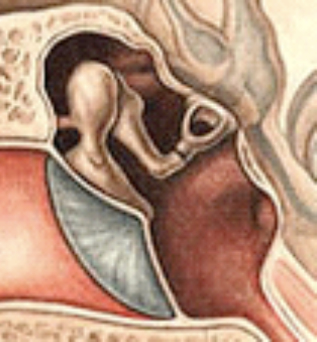
Class 0
Normal Ossicles
M+I+S+
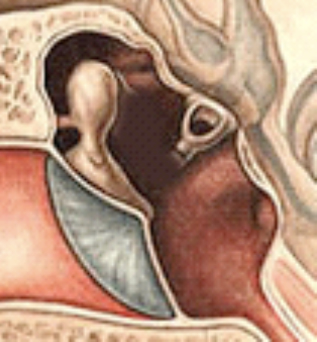
Class A
Absent Incus
M+S+
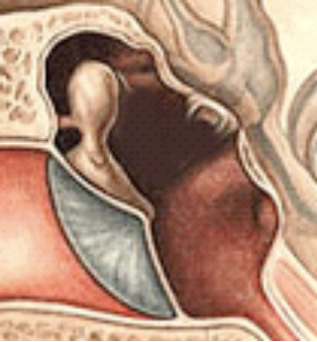
Class B
Absent Incus and Stapes
M+S-
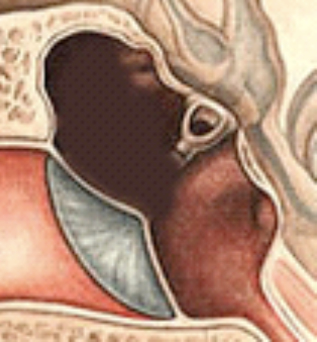
Class C
Absent Malleus and Incus
M-S+
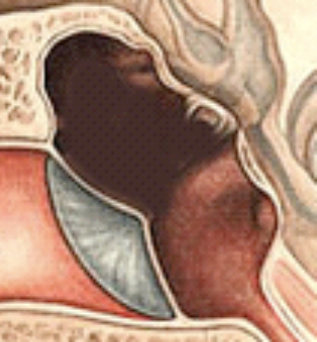
Class D
Absent Ossicles
M-S-
Class E
Ossicular Head Fixation
Class F
Stapes Fixation
[F1-Superstructure intact, F2-Superstructure absent]
Key Articles
*Kartush JM. Ossicular chain reconstruction capitulum to malleus. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1994.27:689-715.
1. TRP: Tympanoplasty reporting protocol – minimum data set for publishing
2. MERI: Middle Ear Risk Index - a numeric indicator for severity of disease
3. AK: Austin-Kartush Ossicular Classification
4. Stratifications to improve study comparisons
a. Risk Categories” Mild, Moderate, Severe
b. Hearing Outcome Categories
Becvarovski Z, Kartush JM. Smoking and tympanoplasty: implications for prognosis and the middle ear risk index (MERI). Laryngoscope. 2001.111:1806-11. (Updated the 1994 MERI)
Kartush J, Michaelides E, Becvarovski Z, LaRouere M: Over-Under Tympanoplasty: Laryngoscope 2002;112:802-807
Bellucci RJ. Selection of cases and classification of tympanoplasty. Otolaryngol Clin North m. 1989 Oct;22(5):911–26
Austin DF. Reporting results in tympanoplasty. Am J Otol. 1985 Jan;6(1):85–8.
AJudd, Ryan T.; Imbery, Terence E.; Gluth, Michael B. The Utility of Numeric Grading Scales of Middle Ear Risk in Predicting Ossiculoplasty Hearing Outcomes, Otology & Neurotology: December 2020 - Volume 41 - Issue 10 - p 1369-1378
SPITE Articles
Black B. Ossiculoplasty prognosis: the spite method of assessment. Am J Otol. 1992 Nov;13(6):544–51.
Black, Bruce Reporting Results in Ossiculoplasty, Otology & Neurotology: July 2003 - Volume 24 - Issue 4 - p 534-542
Judd, Ryan T.; Imbery, Terence E.; Gluth, Michael B. The Utility of Numeric Grading Scales of Middle Ear Risk in Predicting Ossiculoplasty Hearing Outcomes, Otology & Neurotology: December 2020 - Volume 41 - Issue 10 - p 1369-1378
OOPS Articles
Dornhoffer JL, Gardner E. Prognostic factors in ossiculoplasty: a statistical staging system. Otol Neurotol Off Publ Am Otol Soc Am Neurotol Soc Eur Acad Otol Neurotol. 2001 May;22(3):299–304.
Gluth MB, Moore PC, Dornhoffer JL. Method and Reproducibility of a Standardized Ossiculoplasty Technique. Otol Neurotol. 2012 Sep;33(7):1207–1212.
Page, Joshua Cody; Cox, Matthew D.; King, DeAnne; Allsopp, Tristan; Dornhoffer, John L. Long-term Outcomes of Ossiculoplasty With and Without an Intact Malleus, Otology; Neurotology: January 2019 - Volume 40 - Issue 1 - p 73-78
Kotzias SA, Seerig MM, Mello MF, Chueiri L, Jacques J, Silva MB, et al. Ossicular chain reconstruction in chronic otitis media: hearing results and analysis of prognostic factors. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;86:49–55.
“The OOPS index seems not to be accurate on prognosticating hearing outcomes, while the MERI index can be a valuable tool for surgeons to estimate the risks, predict success of the surgery as well as to select the best candidates for reconstruction.”
Ryan T.; Imbery, Terence E.; Gluth, Michael B. The Utility of Numeric Grading Scales of Middle Ear Risk in Predicting Ossiculoplasty Hearing Outcomes, Otology & Neurotology: December 2020 - Volume 41 - Issue 10 - p 1369-1378
MERI Articles
Pasha R, Hill SL, Burgio DL. Evaluation of Hydroxyapatite Ossicular Chain Prostheses. Otolaryngol Neck Surg. 2000 Oct 1;123(4):425–9.
Pinar E, Sadullahoglu K, Calli C, Oncel S. Evaluation of prognostic factors and middle ear risk index in tympanoplasty. Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. 2008.139:386-98.
Chrobok V, Pellant A, Meloun M, Pokorny K, Simáková E, Mandysová P. Prognostic Factors for Hearing Preservation in Surgery of Chronic Otitis Media. Int Adv Otol. 2009.5(3):310-17.
Richard J. Wiet, R. Mark Wiet, Experience-driven ossiculoplasty, Operative Techniques in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Volume 21, Issue 3, 2010, Pages 211-216
Sharma A, Saxena RK, Verma LR, Bhandari S. Correlation Between MERI and Hearing After Tympanoplasty. J Nepalgunj Med Coll. 2015;13(2):6–9.
Ahmed A, Sharma SC. Middle Ear Risk Index [MERI] as Prognostic Factor in Tympanomastoidectomy with Tympanoplasty. Madridge J Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 May 17;1(1):15–22.
Felek SA, Celik H, Islam A, Elhan AH, Demirci M, Samim E. Type 2 ossiculoplasty: prognostic determination of hearing results by middle ear risk index. Am J Otolaryngol. 2010 Oct;31(5):325–31.
Kumar N, Madkikar NN, Kishue S, Chilke D, J Kiran, Shinde. Using middle ear risk index and ET function as parameters for predicting the outcome of tympanoplasty. Indian journal of otolaryngology and head & neck surgery. 2012. 64(1):13-16.
Emir H, Kaptan ZK, Göcmen H, et al. Ossiculoplasty with intact stapes: analysis of hearing results according to the middle ear risk index. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh). 2009 Jan 1;129(10):1088–94.
Demir UL, Karaca S, Ozmen OA, Kasapoglu F, Coskun HH, Basut O. Is it the Middle Ear Disease or the Reconstruction Material That Determines the Functional Outcome in Ossicular Chain Reconstruction? Otol Neurotol. 2012 Jun;33(4):580.
Callioglu, Elif Ersoy et al. “Cartilage Graft or Fascia in Tympanoplasty in Patients with Low Middle Ear Risk Index (anatomical and Audological Results).” European archives of oto-rhino-laryngology. 270.11 (2013): 2833–2837.
Abshirini H, Saki N, Nikakhlagh S, Yavari M. Evaluation of Prognostic Factors in Tympanoplasty. Biosci Biotech Res Asia 2015;12(spl.edn.1)
Kalyanasundaram R, Narendra G. Corelation between middle ear risk index (MERI) and tympanoplasty- a prospective study. Panacea Journal of Medical Sciences. 2017.7(2):65-67.
Kotzias SA, Seerig MM, Mello MFPC de, et al. Ossicular chain reconstruction in chronic otitis media: hearing results and analysis of prognostic factors. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Oct 18.
Hayati R, Hajarharyuna TS. Middle Ear Risk Index Scores as a Predictor for Hearing Threshold after Tympanoplasty in Patients with Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media. J Clin Diagn Res. 2018 Apr 12(4): MC01-MC03.
Kaplankiran H, Ceylan ME, Yildirim GA, Ceylan G, Dalğiç A, Olgun L. Audiological Results of Total Ossicular Replacement Prosthesis with Cartilage Shoe Technique. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Jun;56(2):95–101.
Ramya R. Middle ear risk index (MERI) as a prognostic factor in endoscopic tympanoplasty in chronic otitis media (COM). Presented as a Dissertation at Stanley Medical College, Chennai; 2018.
Patel R, Ghai SK, Kulkarni SV, Bharadwaj C, Sancheti V, Burse KS. Prospective Study of Audiological Analysis of Ossiculoplasty in Cases of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media. MVP J Med Sci. 2019 May 22;6(1):45-52–52.
Rakesh Saboo, Amit Modwal, Priyanjal Gautam. Tubotympanic CSOM: clinical profile of perforation, eustachian tube function and MERI score as parameter for outcome of tympanoplasty. Transworld Medical Journal. 2(2):154¬159.
Ohki, Masafumi, Shigeru Kikuchi, and Sunao Tanaka. “Endoscopic Type 1 Tympanoplasty in Chronic Otitis Media: Comparative Study with a Postauricular Microscopic Approach.” Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery 161.2 (2019): 315–323.
Calim OF, Veri̇m A, Özkul MH, et al. An evaluation of prognostic factors for tympanoplasty with titanium prostheses in chronic ear surgery. Anadolu Klin Tip Bilim Derg. 2019 Jan 30;24(1):8–14.
Sarfaraz, Tabassum A. An observational study on tympanoplasty in terms of middle ear risk index (MERI) of patients with chronic suppurative otitis media. International Journal of Medical and Health Research. 2017.3(6):25-28.
Sridhar R. Impact of otorrhoea and ossicular status on the effect of tympanoplasty. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2018;4(6):1366-1371
Sonawale S et al: Study of type II Tympanoplasty using Autologous incus. Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research – Otorhinolaryngology Special Issue, June 2018, 7 (3), 31-41
Cebeci S, Özbilen MS, Bayramoğlu I, Kemaloğlu YK, Uygur KK, Bayazit YA, Karamert R. Impact of the demographic and aetiological factors and intraoperative findings on postoperative outcomes in chronic otitis media surgery. Turk J Med Sci. 2020 Feb 13;50(1):155-162.
Vignadutt, P.; Shaik, Ali. A retrospective study on middle ear risk indices in analysing the postoperative outcome following tympanoplasty. International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery, [S.l.], v. 5, n. 5, p. 1234-1239, Aug. 2019. ISSN 2454-5937.
Shishegar, M., Faramarzi, M. & Rashidi Ravari, M. Evaluation of middle ear risk index in patients undergoing tympanoplasty. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276, 2769–2774 (2019).
Nallapaneni, L.S., Sudarsan, S. & Krishnamoorthy, S. A Prospective Study on Middle Ear Risk Index (MERI) and Outcome of Tympanoplasty with a Note on quality-of-Life (QOL). Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg (2020)
Anil S. Harugop, Somashekhar Abhilasha, Pratibha S. Desai. Assessment of middle ear risk index in predicting the outcome of treatment of CSOM. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Nov;6(11):2075-2080
Kotzias SA, Seerig MM, Mello MF, Chueiri L, Jacques J, Silva MB, et al. Ossicular chain reconstruction in chronic otitis media: hearing results and analysis of prognostic factors. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;86:49–55.
“The OOPS index seems not to be accurate on prognosticating hearing outcomes, while the MERI index can be a valuable tool for surgeons to estimate the risks, predict success of the surgery as well as to select the best candidates for reconstruction.”
Poonam K. Saidha, Sahil Kapoor, Arpita Suri, Vikas Kakkar: Evaluation of the role of middle ear risk index as a prognostic tool in cases of tympanoplasty in chronic suppurative otitis media. March 2021 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery 7(4):622
de la Torre Carlos, Vasquez Carolina, Villamor Perla: Middle Ear Risk Index (MERI) As A Prognostic Factor For Tympanoplasty Success In Children. February 2021. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology
Zhu X-H, Zhang Y-L, Xue R-Y, Xie M-Y, Tang Q, Yang H. Predictors of anatomical and functional outcomes following tympanoplasty: A retrospective study of 413 procedures. Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology. 2021;1-8.
Previous studies have reported smoking to be of prognostic importance, and it was added in MERI 2001.11 In our study, smoking was a predictor for the hearing outcome following tympanoplasty. The rate of hearing failure was two times higher
Moreover, the obstructed aditus ad antrum and MERI >3 (P < .001) were independent predictors of hearing failures
Austin-Kartush Articles
Moretz WH. Ossiculoplasty With an Intact Stapes: Superstructure Versus Footplate Prosthesis Placement. Laryngoscope, 108 (Suppl.89):1-12,1998
Maceri D. Stabilization of Total Ossicular Replacement Prosthesis in Ossiculoplasty. Laryngoscope 109: 1884-5, November 1999
Vincent, Robert; Oates, John; Sperling, Neil M.; Annamalai, Sivakumar Malleus Relocation in Ossicular Reconstruction: Managing the Anteriorly Positioned Malleus: Results in a Series of 268 Cases, Otology & Neurotology: May 2004 - Volume 25 - Issue 3 - p 223-230
Vincent, Robert; Sperling, Neil M; Oates, John; Osborne, Jonathan. Ossiculoplasty with Intact Stapes and Absent Malleus: The Silastic Banding Technique, Otology & Neurotology: September 2005 - Volume 26 - Issue 5 - p 846-852
Martin, T.P.C., Weller, M.D., Kim, D.S. & Smith, M.C.F.. Results of primary ossiculoplasty in ears with an intact stapes superstructure and malleus handle: inflammation in the middle ear at the time of surgery does not affect hearing outcomes. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2009, 34, 218–224
Iurato, Salvatore; Marioni, Gino; Onofri, Marina Hearing Results of Ossiculoplasty in Austin-Kartush Group A Patients, Otology & Neurotology: March 2001 - Volume 22 - Issue 2 - p 140-144
Richard J. Wiet, R. Mark Wiet, Experience-driven ossiculoplasty, Operative Techniques in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Volume 21, Issue 3, 2010, Pages 211-216.
Vincent, Robert; Rovers, Maroeska; Mistry, Nina; Oates, John; Sperling, Neil; Grolman, Wilko. Ossiculoplasty in Intact Stapes and Malleus Patients: A Comparison of PORPs Versus TORPs With Malleus Relocation and Silastic Banding Techniques. Otology & Neurotology. 32(4):616-625, June 2011.
Sue Jean Mun, Joo Hyun Park, Chang Myeon Song: Audiologic Results of Ossiculoplasty Using Malleus Footplate Assembly: The Comparison between Autologous Incus and Hydroxyapatite. Korean J Audiol 2011;15:141-146
Vincent, Robert; Bittermann, Arnold J. N.; Wenzel, Gentiana; Oates, John; Sperling, Neil; Lenarz, Thomas; Grolman, Wilko Ossiculoplasty in Missing Malleus and Stapes Patients: Experimental and Preliminary Clinical Results With a New Malleus Replacement Prosthesis With the Otology-Neurotology Database, Otology & Neurotology: January 2013 - Volume 34 - Issue 1 - p 83-90
Nadir Yıldırım, Semra Külekçi, Zühal Zeybek Sivas, Cüneyt Kucur. Comparison of Primary and Secondary Cholesteatomas in Terms of Ossicular Destruction and Complications. Turk Arch Otolaryngol 2014; 52: 121-5
Ucar S, Iseri M, Ozturk M. Evaluation of functional results of CWD surgery with ossicular replacement prosthesis due to cholesteatoma using computed tomography. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014;271(9):2393–2400.
Blom EF, Gunning MN, Kleinrensink NJ, et al. Influence of Ossicular Chain Damage on Hearing After Chronic Otitis Media and Cholesteatoma Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015;141(11):974–982.
“For future studies, we recommend the use of the Austin-Kartush criteria to measure ossicular chain damage OCD and the AAO-HNS guidelines in audiology for reporting hearing outcomes at standardized intervals to maximize comparability of results.”
“Pooled results of Austin-Kartush studies showed that in patients with COM, with or without cholesteatoma, the malleus status is a significant predictor of postoperative hearing outcome, independent of the stapes condition”
Gerard, Jean-Marc; DeBie, Gersende; Franceschi, Daniel; Deggouj, Naima ;Gersdorff, Michel . Ossiculoplasty with hydroxyapatite bone cement: our reconstruction philosophy. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology" - Vol. 272, no. 7, p. 1629-1635 (2015)
Deniz Tuna Edizer, MD, Yusuf Muhammed Durna, MD, Bahtiyar Hamit, MD, Hasan Demirhan, MD, and Ozgur Yigit, MD. Malleus to Stapes Bone Cement Rebridging Ossiculoplasty: Why Don’t We Perform Frequently? Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology 2015 125:6, 445-451
Jean‐Marc Gérard, Gersende De Bie, Daniel Franceschi · Naima Deggouj · Michel Gersdorff. Ossiculoplasty with hydroxyapatite bone cement: our reconstruction philosophy. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2015) 272:1629–1635
Mustafa Aslıer, Taner Kemal Erdag, Sulen Sarioglu, Enis Alpin Güneri, Ahmet Omer Ikiz, Evren Uzun, Erdener Özer. Analysis of histopathological aspects and bone destruction characteristics in acquired middle ear cholesteatoma of pediatric and adult patients. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology, Volume 82, 2016, Pages 73-77, ISSN 0165-5876
Thamizh Arasan. New Classification of Ossicular Status and Study In Patients with Ossicular Erosion to be Used for Ossiculoplasty.Otolaryngology Online Journal (2017) Volume 7, Issue 1, 144
Jerome Nevoux, Gilles Roger, Pierre Chauvin; Francoise Denoyelle; Erea Noel Garabedian. Cartilage Shield Tympanoplasty in Children. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;137(1):24-29
Sue Jean Mun, Joo Hyun Park, Chang Myeon Song: Audiologic Results of Ossiculoplasty Using Malleus Footplate Assembly: The Comparison between Autologous Incus and Hydroxyapatite. Korean J Audiol 2011;15:141-146
Gupta A, Kumar A, Tuli IP, Soni P. Comparative evaluation of early results with ossicular reconstruction employing titanium and hydroxyapatite prostheses. Astrocyte 2015;2:111-5
Scott-Brown's Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Volume 2: Paediatrics, The Ear, and Skull Base Surgery By Ray W Clarke. 2018
Mhashal SK et al. Assessment of short term hearing improvement in patients of cartilage interposition ossiculoplasty for lenticular process of incus necrosis in cases of chronic suppurative otitis media: mucosal disease. International J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surgery | October-December 2017 | Vol 3 | Issue 4
Irwan et al. Pre and intraoperative findings of chronic otitis media. 2019 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1246 012019
Nivee N, Varghese BS. Post-operative Auditory Gain in Patients Undergoing Intact Canal Wall Mastoidectomy and Ossiculoplasty with Primary Malleus Transposition (rotation) Ossiculoplasty. Int J Sci Stud 2019;6(12):53-56
Düzenli, U., & Kıroğlu, A. Manubrio-incudo-stapedioplasty for reconstruction of Austin–Kartush type B ossicular defects. The Journal of Laryngology & Otology, (2019). 133(6), 457-461.
Arindam Das, MS; Sandipta Mitra, MS ; Debasish Ghosh, MS; Arunabha Sengupta. Endoscopic Ossiculoplasty: Is There Any Edge Over the Microscopic Technique?. Laryngoscope, 130:797–802, 2020
MERI & Austin-Kartush Reviews Articles
Balough B, Kartush J: Ossicular chain reconstruction – Current Opinion in otolaryngology, Vol 9, Issue 5, 2001:272-278.
Kartush J, Babu S : Ossicular chain reconstruction – pitfalls. Wiet R (ed) Ear and Temporal Bone Surgery: Minimizing Risks and Complications. Thieme, New York, 2006:90-101.
Kartush J: Ossicular chain reconstruction. Master Techniques in Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery: Otology, Neurotology and Lateral Skull Base Surgery, edited by J. Thomas Roland, Jr., MD; series editor Eugene Myers, MD. Wolters Kluwer, Philadelphia. P109 – 124, 2018.
Neudert M, Zahnert T. Tympanoplasty – news and new perspectives. GMS Curr Top Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017;16: Doc 07.
Susen Lailach, Thomas Zahnert, Marcus Neudert. Data and Reporting Quality in Tympanoplasty and Ossiculoplasty Studies. Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery 2017, Vol. 157(2) 281–288
However, while a great number of parameters could be recorded, a publication should focus particularly on factors that contribute to quality assurance and assessment. Although the surgical, prosthetic, infection, tissue, and eustachian (SPITE) criteria introduced by Black report in great detail on nearly all influencing factors, this 19-item questionnaire seems to be cumbersome in a single study, which may primarily focus on the analysis of a special reconstruction technique.
Adva Buzi, Michael B. Gluth, and Bruce Black. Chronic Ear Disease in the Modern Era: Evolution of Treatment, Epidemiology, and Classification. In Book: The Chronic Ear. Dornhoffer, J.L., & Gluth, M.B. Thieme (2016).
Marcus Neudert: Quality in middle ear surgery – a critical position determination. Qualität in der Mittelohrchirurgie – eine kritische Standortbestimmung. Laryngo-Rhino-Otol 2020; 99(S 01): S1-S26
Linder, Thomas E.; Shah, Shankar; Martha, Aline Silveira; Röösli, Christof; Emmett, Susan D. Introducing the “ChOLE” Classification and Its Comparison to the EAONO/JOS Consensus Classification for Cholesteatoma Staging, Otology & Neurotology: January 2019 - Volume 40 - Issue 1 - p 63-72
Judd, Ryan T.; Imbery, Terence E.; Gluth, Michael B. The Utility of Numeric Grading Scales of Middle Ear Risk in Predicting Ossiculoplasty Hearing Outcomes, Otology & Neurotology: December 2020 - Volume 41 - Issue 10 - p 1369-1378
Cholesteatoma Classifications Articles
Yung, Matthew et al. “EAONO/JOS Joint Consensus Statements on the Definitions, Classification and Staging of Middle Ear Cholesteatoma.” The journal of international advanced otology. 13.1 (2017): 1–8.
Ardıç FN, Mengi E, Tümkaya F, Kara CO, Bir F. Correlation between Surgical Outcome and Stage of Acquired Middle Ear Cholesteatoma: Revalidation of the EAONO/JOS Staging System. J Int Adv Otol. 2020 Apr;16(1):34-39.
JLinder TE, Shah S, Martha AS, Röösli C, Emmett SD. Introducing the "ChOLE" Classification and Its Comparison to the EAONO/JOS Consensus Classification for Cholesteatoma Staging. Otol Neurotol. 2019 Jan;40(1):63-72.
Bächinger, D., Rrahmani, A., Weiss, N.M. et al. Evaluating hearing outcome, recidivism and complications in cholesteatoma surgery using the ChOLE classification system. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 278, 1365–1371 (2021)
Eggink, Maura C.; de Wolf, Maarten J.F.; Ebbens, Fenna A.; Dikkers, Frederik G.; van Spronsen, Erik Evaluation of Long-term Cholesteatoma Recidivism, Otology & Neurotology: April 23, 2021 - Volume Publish Ahead of Print